Closing the carbon cycle to stop climate change
Defects in nanosilica can save planet earth from global warming
Advertisement
An excessive amount of carbon dioxide is the main cause of climate change. One of the best approaches is to capture and convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into fuel such as methane. On the other hand, a sustainable way to solve the energy problem is to generate alternative energy source, however, challenges related to the storage of renewable electricity are preventing the development of these technologies. Thus, CO2 conversion to methane using renewable hydrogen has the great potential to provide a solution to these two problems of excessive CO2 levels, and the temporal mismatch between renewable electricity production and demand as well as hydrogen storage.
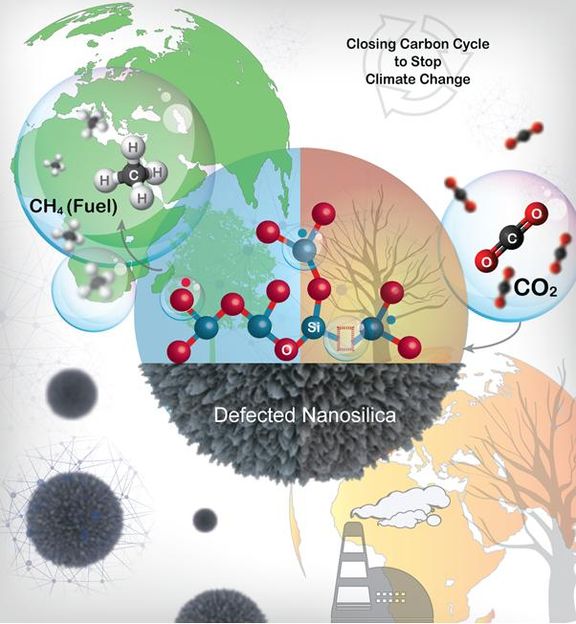
Defects in nanosilica can save planet earth from global warming.
Ayan Maity, TIFR, Mumbai
Best-known catalysts for CO2 methanation are supported nanoparticles of metals. However, most of them suffer from the issue of stability as well as selectivity towards methane over CO. Best way to resolve the issue of catalyst stability is by replacing active sites (metal nanoparticles) with metal-free active sites which are catalytic as well as stable even in an air environment at high temperatures.
In this work, researchers at TIFR have developed the magnesiothermic defect engineering protocol to design a new catalyst system where metal nanoparticle active sites were replaced with defects as catalytically active sites.
This is the first metal-free-ligand-free catalyst for CO2 conversion. The defects in nanosilica convert CO2 to methane with excellent productivity and selectivity. Furthermore, metal nanoparticles were not required, and the defect sites alone acted as catalytic sites for carbon dioxide activation and hydrogen dissociation and their cooperative action converted CO2 to methane.
The catalyst is recyclable and stable for more than 200 h with 10000 μmoles g-1 h-1 of productivity for methane. Notably, unlike expensive metal catalysts, the catalytic activity for methane production increased significantly after every regeneration cycle, reaching more than double the methane production rate after eight regeneration cycles as compared to the initial catalyst performance.
The spectroscopy studies gave atomistic insights into the various defect sites (Si radical centers, O-vacancy, and non-bridging oxygen hole centres) in terms of their concentrations, proximity, and cooperativity. In-Situ spectroscopy study provided mechanistic insights at a molecular level, indicating possible pathways for CO2 conversion to methane and carbon monoxide, which was further confirmed by computational study in collaboration with Prof. Ayan Datta of Indian Association of Cultivation Science (IACS), Kolkata.