Clusters of gold atoms form peculiar pyramidal shape
Advertisement
clusters composed of a few atoms tend to be spherical. They are usually organized in shells of atoms around a central atom. This is the case for many elements, but not for gold! Experiments and advanced computations have shown that freestanding clusters of twenty gold atoms take on a pyramidal shape. They have a triangular ground plane made up of ten neatly arranged atoms, with additional triangles of six and three atoms, topped by a single atom.
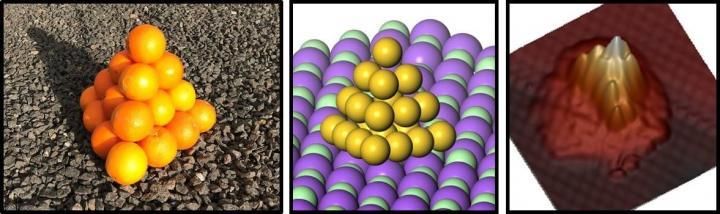
A model of 20 oranges is compared with the theoretical and experimental structure.
KU Leuven
The remarkable tetrahedral structure has now been imaged for the first time with a scanning tunnelling microscope. This high-tech microscope can visualise single atoms. It operates at extremely low temperatures (269 degrees below zero) and uses quantum tunnelling of an electrical current from a sharp scanning metallic tip through the cluster and into the support. Quantum tunnelling is a process where electrical current flows between two conductors without any physical contact between them.
The researchers used intense plasmas in a complex vacuum chamber setup to sputter gold atoms from a macroscopic piece of gold. "Part of the sputtered atoms grow together to small particles of a few up to a few tens of atoms, due to a process comparable with condensation of water molecules to droplets," says Zhe Li, the main author of the paper, currently at the Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen. "We selected a beam of clusters consisting of exactly twenty gold atoms. We landed these species with one of the triangular facets onto a substrate covered with a very thin layer of kitchen salt (NaCl), precisely three atom layers thick."
The study also revealed the peculiar electronic structure of the small gold pyramid. Similar to noble gas atoms or aromatic molecules, the cluster only has completely filled electron orbitals, which makes them much less reactive than clusters with one or a few atoms more or less.
Gold clusters ranging from a few to several dozens of atoms in size are known to possess remarkable properties.
The new discovery helps scientists evaluate the catalytic and optical performances of these clusters, which is relevant for designing cluster-based catalyst and optical devices. Recent applications of clusters include utilisation in fuel cells and carbon capture.