Lab in hollow MOF capsules beyond integration of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis
Homogeneous molecular catalysts are highly active and selective as they possess well-tailored structures and accessible sites. Unfortunately, the difficulty related to catalyst recovery impedes their practical application. The encapsulation of them inside hollow porous solid materials is a judicious solution. While a number of reports on stabilizing homogeneous catalysts to solid supports, including porous polymers/silica/carbons, and zeolites, etc., it remains significant challenge with regards to the dilemma in the integration of respective advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts without compromised catalytic performance of the former and porosity of the latter.
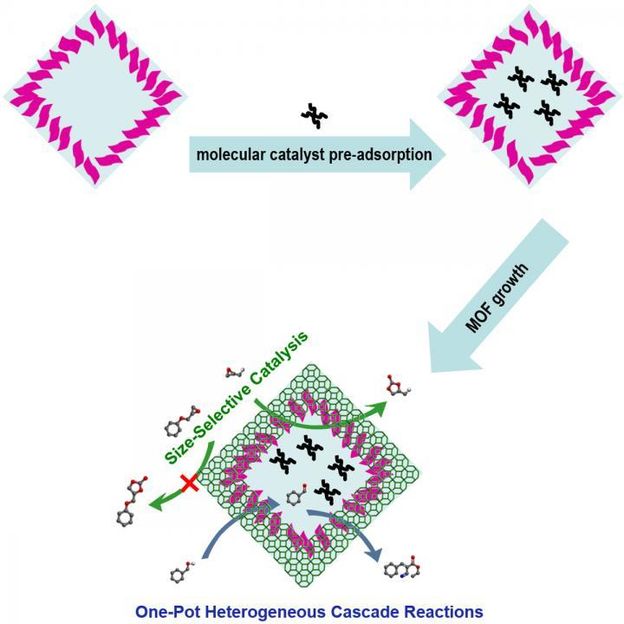
Schematic showing the fabrication of yolk (soluble)-shell (crystalline) MOF capsules for size-selective and one-pot cascade catalysis.
©Science China Press
Typically, the previous shells are usually assembled by imperfect particle packing and feature additional interparticle pores that are not able to encapsulate small homogeneous active guests. The attempts on endowing the resulting composite catalysts with additional features (for example, substrate enrichment, selective catalysis, cascade catalysis, etc.), beyond the simple recombination of classical merits of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts, has never been reported yet.
In the present work, the authors have developed a template-directed approach for the construction of various hollow metal-organic framework (MOF) capsules with a continuous shell and size-selective permeability, which are useful in sealing up diverse soluble active species.
This novel template-directed process is straightforward and versatile (diverse MOFs, such as ZIF-8, ZIF-67, MOF-74, etc., are applicable) for the fabrication of various MOF capsules with a dense, stable and thin MOF shell, which eliminate additional interparticle pores/defects in previous reports on hollow porous capsules. During the synthetic process, different soluble active species can be readily encapsulated into the interior cavity of the hollow MOF capsules, thus making the synthetic approach very powerful and extendable.
The resultant yolk-shell MOF capsules exhibit superior activity to the individual bulk MOF and the guest active catalyst, benefiting from the synergistic effects between the high intrinsic activity of the molecular catalyst and substrate enrichment effect of the crystalline MOF shell. Moreover, the perfect MOF shell endows the resultant composites with substrate enrichment, size-selectivity, great recyclability, and multifunctional cascade catalysis.
Such yolk (soluble)-shell (crystalline) MOF capsule-based composites not only integrate the respectively intrinsic merits of soluble active species (homogeneous catalysts) and MOFs (heterogeneous catalysts and crystalline porous materials), but also open up an avenue to the generation of additional catalysis features (substrate enrichment, selective catalysis, cascade catalysis, etc.), for synergistically enhanced applications, especially in high-performance catalysis.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.



























































