Chemists create new types of Lewis acids
Synthesis for the first time on the basis of phosphorus
Researchers at the University of Münster have developed a method which makes it possible to create three-coordinate Lewis superacids on the basis of phosphorus. Previously, it had not been possible to isolate this type of compound, either in a liquid or in a solid state, due to its extreme electrophilicity and the associated reactivity.
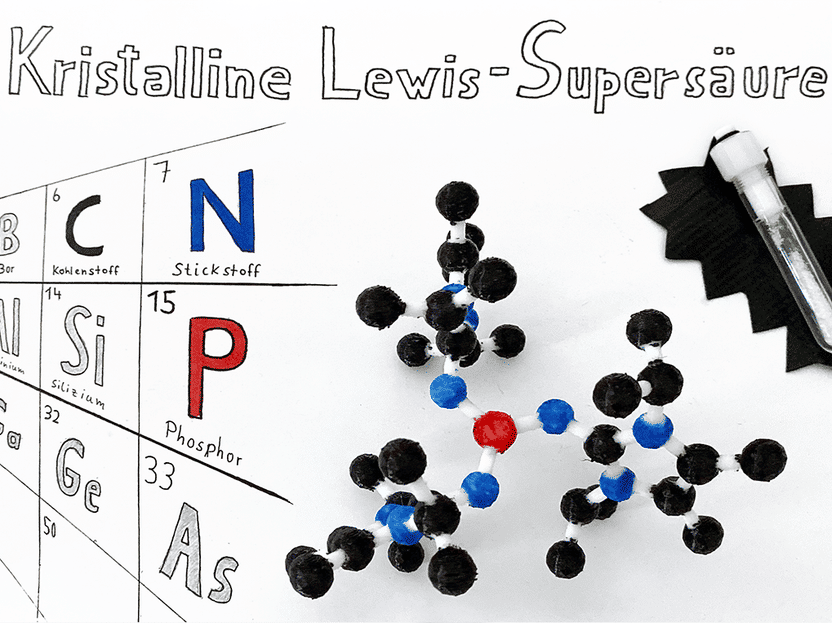
Structure and crystalline state of the new type of Lewis superacid
© Dielmann group
In chemistry, Lewis acids are compounds which endeavour to accept electron pairs. Because of this so-called electrophilicity, they are often used to speed up chemical reactions. One example of this is the production of polyurethane synthetics used in the manufacture of foams for building insulation, car seats and household sponges.
“We use special substituents which regulate the electrophilicity of the phosphorus atom,” says Dr. Fabian Dielmann, who heads an Emmy Noether Junior Researchers Group at Münster University. “As a result, the reactivity of the compounds can be reduced somewhat, enabling them to be isolated as crystalline solids. This represents important progress in the field of Lewis acids chemistry,” he adds. Previously, only a few Lewis superacids with a similarly high electrophilicity had been synthesised. However, these differ in their reactivity from the new types of phosphorous compounds. These latter compounds make new activation mechanisms possible for converting particularly inert molecules – which extends their utilization in synthesis chemistry.
Background, method and prospects
Especially in recent times, the development of highly electrophilic compounds has paved the way for much important progress in the field of Lewis acids chemistry. For a long time it was assumed that such compounds in condensed phase could not exist in free form. It was only in 2002, as a result of the clever choice of voluminous substituents and the use of weakly coordinating counterions, that chemists J. B. Lambert and C. A. Reed first succeeded in isolating three-coordinate silicon ions. Almost two decades after this breakthrough, the team of researchers led by Fabian Dielmann has now shown – contrary to all previous assumptions – that the synthesis of structurally similar Lewis superacids based on phosphorus is possible.
As the phosphorus superacids are particularly reactive, they can only be handled under the strict exclusion of air and moisture. After the synthesis, the compounds were obtained as white crystalline solids, and their properties were examined using NMR spectroscopy, mass-spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray structure analysis. The chemists carried out quantum-mechanical calculations in order to gain a better understanding of the electronic structure, as well as to compute the electrophilicity.
With the work they have done, the Münster University chemists have demonstrated a method enabling extremely electrophilic compounds to be stabilised through the use of special substituents. The researchers assume that, by transferring the underlying method to other classes of compounds hitherto classified as “not viable”, the creation of further highly electrophilic compounds can be advanced.
Original publication
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.