Always on beat: ultrashort flashes of light under optical control
Advertisement
Ultrashort laser pulses have enabled scientists and physicians to carry out high-precision material analyses and medical procedures. Physicists from the University of Bayreuth and the University of Göttingen have now discovered a new method for adjusting the extremely short time intervals between laser flashes with exceptional speed and precision. The intervals can be increased or decreased as needed, all at the push of a button. Potential applications range from laser spectroscopy to microscopy and materials processing. The researchers have now presented their latest findings in the journal Nature Photonics.
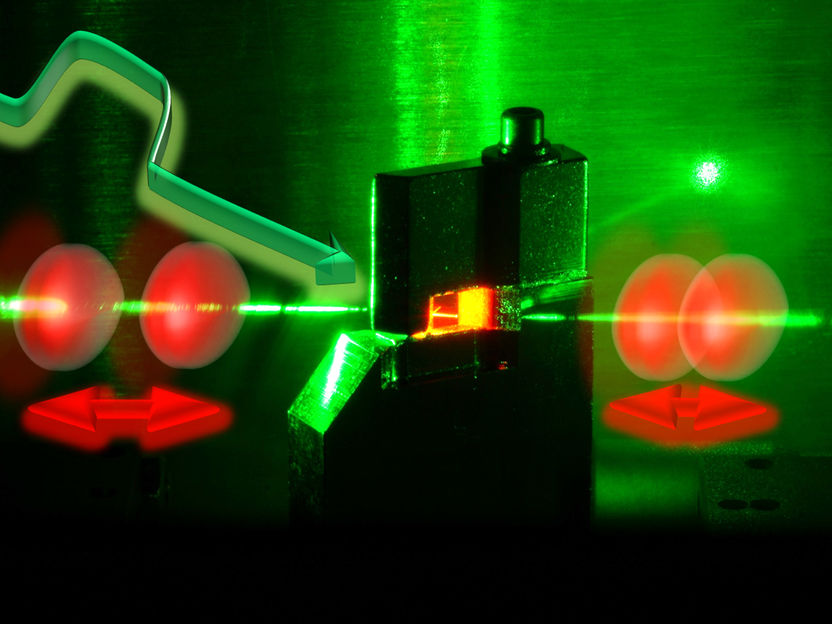
Light pulses can form pairs in ultra-short pulse lasers. The pulse intervals (red) can be precisely adjusted by making certain changes to pump beam (green).
UBT
Laser pulses have long been utilized in research laboratories, industrial production, and medical therapies. In these applications it is often crucial that the pulses – also known as optical solitons – occur at certain intervals. Using a special high-speed measurement technique, the researchers have now been able to show how a short-pulse laser widely applied in research can be made to automatically generate pairs of light pulses separated by the desired interval. All that is required are small disturbances in the green optical "pump beam” (which generates the laser pulses) triggered by electric signals.
The new process centres on the targeted manipulation of solitons, wave packets that can occur in pairs in ultrashort laser pulses. "The resonance excitation and the short disturbance of soliton pairs trigger effects that can be used to specifically control ultrashort laser pulses. This opens up an exciting new area of research with a yet unforeseeable range of possible applications," said Prof. Dr. Georg Herink from Bayreuth, corresponding author of the new study. "At the right frequency, a tiny external modulation of the laser is all you need, and ultrashort laser pulses are set into reciprocal, resonant oscillation. Similar phenomena can be observed in water molecules heated in the microwave," added lead author Felix Kurtz from Göttingen.
The newly published findings show that in the future, ultra-short pulse lasers will not only be considered as a tool, but also remain a fascinating object of research.