Forward or backward? New pathways for protons in water or methanol
Advertisement
A collaborative ultrafast spectroscopy and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations study, as recently published by scientists of the Max Born Institute of Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI) and the Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, shows that proton vacancies in the form of hydroxide/methoxide ions are as relevant for proton transfer between acids and bases as hydrated excess protons (H3O+, H5O2+), thus pointing for a clear demand for refinement of the microscopic picture for aqueous proton transport – in solution as well as in hydrogen fuel cells or transmembrane proteins – away from currently often assumed dominant role of hydrated excess protons.
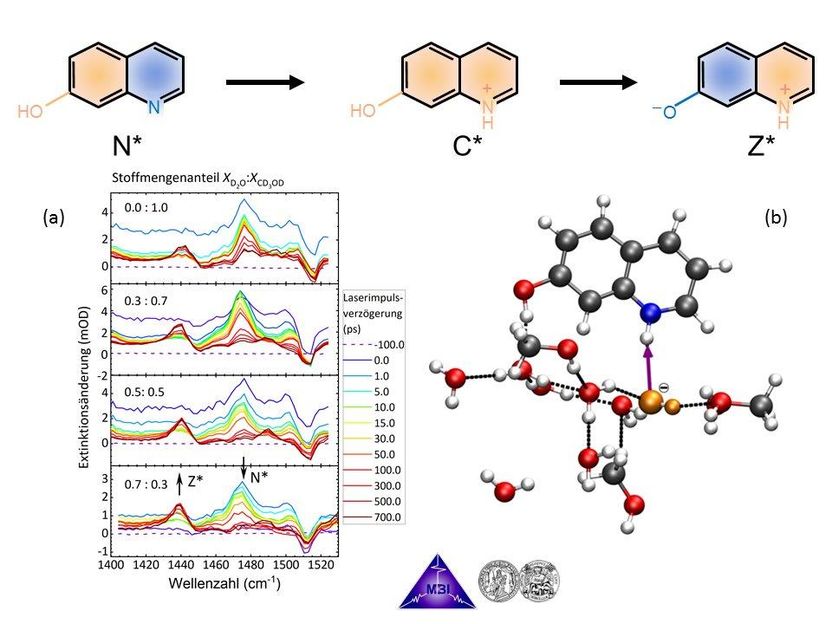
Monitoring proton transport of 7-hydroxyquinoline in water/methanol solvent mixtures in real time from the reactant neutral N* via the intermediate cation C* to the zwitterionic product Z* with UV-pump/IR-probe spectroscopy of IR-active marker modes (a), and following ab initio molecular dynamics trajectories (b). The snapshot in (b) shows the moment when the first reaction step, proton abstraction from a nearby water molecule by the nitrogen atom of 7-hydroxyquinoline (above, blue atom), just has taken place and an OH– ion (orange) has been formed, surrounded by other solvent molecules.
MBI
The exchange of protons between two chemical groups (acid-base neutralization) is a textbook chemistry problem for many years. Surprisingly, up to this date new fundamental insight about the elementary steps of proton transport is being obtained. This may well lie in the fact that the elementary steps (by protons or proton vacancies) take place on extremely short time scales, that are not accessible with conventional laboratory techniques (Figure 1). Observation of these elementary reaction steps, as achieved by the research teams of MBI and MLU thus requires direct access to time scales of 1-100 picoseconds, necessitating an experimental set-up with an accordingly high time resolution as well as high performance computer systems.
The research teams have jointly studied a particular model system (7-hydroxyquinoline in water/methanol mixtures), where an ultrashort laser pulse triggers the deprotonation of an OH-group and the protonation of a nitrogen atom. The precise chronology of the elementary steps with these class of chemical reactions have remained elusive, leading to numerous speculations. The scientists of the MBI and MLU have now been able to determine that the release of a proton from the OH-group to the solvent is indeed ultrafast, yet the pick-up of a proton by the nitrogen atom is even faster. This results in a transport mechanism of proton vacancies, i.e. of hydroxide/methoxide ions. The elementary reaction steps have been elucidated with time-resolved IR spectra and detailed quantum chemical calculations (see Figure 2).
Original publication
M. Ekimova, F. Hoffmann, G. Bekçioğlu-Neff, A. Rafferty , O. Kornilov, E. T. J. Nibbering and D. Sebastiani; "Ultrafast proton transport between a hydroxy acid and a nitrogen base along solvent bridges governed by hydroxide/methoxide transfer mechanism"; Journal of the American Chemical Society; 141 (37), 14581-14592 (2019).
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!