New rechargeable aqueous battery challenges Lithium-ion dominance
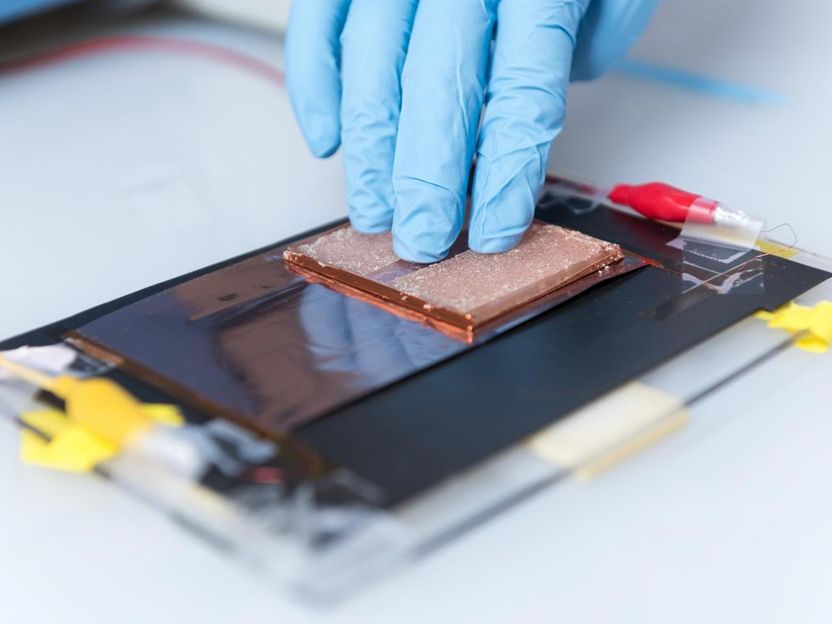
A new rechargeable high voltage manganese dioxide zinc battery, exceeding the 2 V barrier in aqueous zinc chemistry, is the latest invention by City College of New York researchers. With a voltage of 2.45-2.8V, the alkaline MnO2|Zn battery, developed by Dr. Gautam G. Yadav and his group in the CCNY-based CUNY Energy Institute, could break the long dominance of flammable and expensive lithium (Li)-ion batteries in the market.
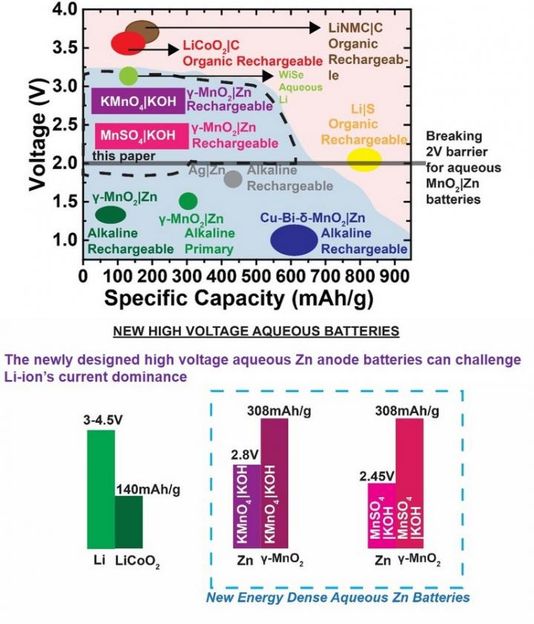
The newly designed high voltage aqueous Zn anode batteries can challenge Li-ion's current dominance.
G.G. Yadav et al, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4, 2144-2146
To break the previously daunting 2 V barrier in aqueous zinc chemistry, primary inventor Yadav and his team interfacially engineered two different aqueous electrolytes that deliver the theoretical capacity (308mAh/g) reversibly for many cycles.
"The voltage of current commercially available alkaline MnO2|Zn batteries is around 1.2-1.3V, and this has been considered low compared to Li-ion which has a voltage >3V," said Yadav.
Voltage has been Li-ion's greatest asset and has helped fuel its rise in an energy hungry world.
"Unfortunately it contains elements that are toxic and geopolitically sensitive with Asian countries having a monopoly on mining and manufacturing them," added Yadav.
"This has put the United States at a tremendous disadvantage and has lost its lead in energy storage industry, when in the past it was a world leader. With Mn and Zn being widely available elements, and with the U.S. being rich with them as well, it allows the U.S. to compete again. The manufacturing cost of these batteries will also be low, so it can kick start the growth of the energy storage industry in the U.S."
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.

Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.