Researchers discover semiconducting nanotubes that form spontaneously
Advertisement
If scientists could find a way to control the process for making semiconductor components on a nanometric scale, they could give those components unique electronic and optical properties - opening the door to a host of useful applications.
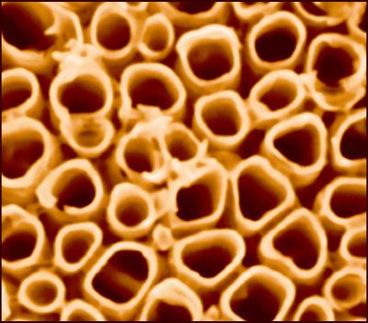
The tubes consist of several walls that are perfectly uniform and just a few atoms thick. They display optical properties that make them perfect for use as fluorophores or photocatalysts.
EPFL
Researchers at the Laboratory of Microsystems, in EPFL's School of Engineering, have taken an important step towards that goal with their discovery of semiconducting nanotubes that assemble automatically in solutions of metallic nanocrystals and certain ligands. The tubes have between three and six walls that are perfectly uniform and just a few atoms thick - making them the first such nanostructures of their kind.
What's more, the nanotubes possess photoluminescent properties: they can absorb light of a specific wavelength and then send out intense light waves of a different color, much like quantum dots and quantum wells. That means they can be used as fluorescent markers in medical research, for example, or as catalysts in photoreduction reactions, as evidenced by the removal of the colors of some organic dyes, based on the results of initial experiments.
An accidental discovery
But the unique feature of these semiconducting nanotubes is how they are formed. "Our discovery happened almost by chance. We had set out to study the role that certain ligands play in making 2D semiconducting nanometric crystals," says Xiaopeng Huang, the study's lead author. But the research team found that some ligands caused molecules to spontaneously come together in precise cylindrical structures which until then had been impossible to create.
Investigating new properties
The researchers will now investigate the other physical and electrical properties of their nanotubes and look into methods for making nanotubes with just a single wall.