Fingerprint spectroscopy within a millisecond
Quality control in real time for the use in the pharmaceutical, chemical and food industry
To guarantee high quality pharmaceuticals, manufacturers need not only to control the purity and concentration of their own products, but also those of their suppliers. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF have developed a measuring system capable of identifying a wide variety of chemical and pharmaceutical substances remotely and in real time. It is perfect for the use in the pharmaceutical, chemical and food industry.
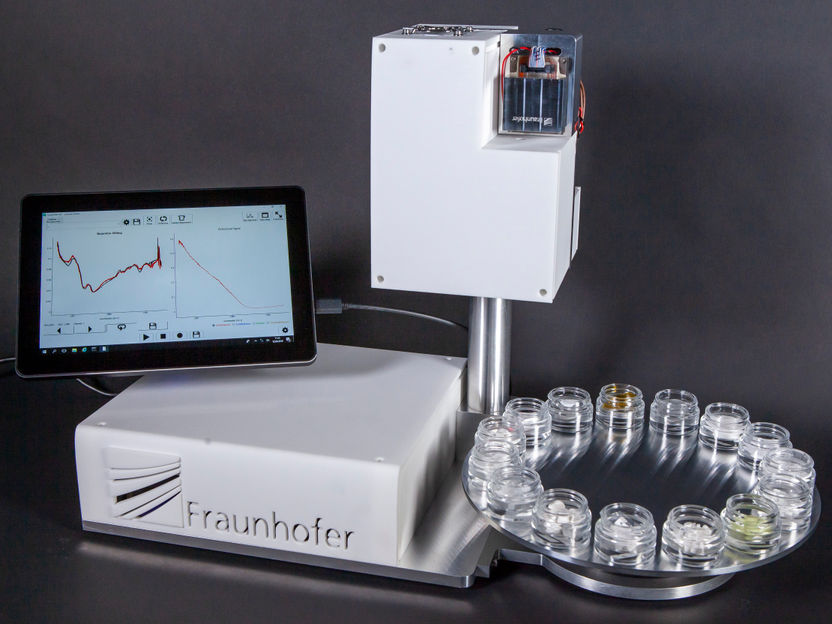
Researchers of Fraunhofer IAF will present their demonstrator of the measuring system at this year’s LASER World of PHOTONICS.
© Fraunhofer IAF
Especially for pharmaceutical and food productions a continuous control of ingredients is indispensable. Usually, this would be done by a sampling and a laboratory analysis via chromatography or spectrometers. However, such a process is time-consuming and allows only for spot checks. At Fraunhofer IAF, researchers have developed a measuring system capable of a quality control in real time. It identifies even smallest amounts of substances based on their molecular composition.
Real-time measurements with quantum cascade lasers
The core of the system is an extremely fast tunable quantum cascade laser (QCL) operating in the mid-infrared range. Based on backscattering spectroscopy, the laser system not only allows to identify smallest amounts of chemical substances in real time, but also to continuously control chemical reaction processes. »Our measuring system allows for a remote identification of a wide variety of chemical and pharmaceutical substances. Time-consuming measurement procedures in laboratories can be replaced by real-time measurements during ongoing production processes«, explains Dr. Marko Härtelt, researcher at Fraunhofer IAF.
Together with his colleagues, he has been working on the development of QCLs for infrared spectroscopy for several years now. With the help of researchers of Fraunhofer IPMS, he has developed a compact and robust laser source with which the whole wavelength range of the QCL emitter can be scanned within a millisecond. The basis for this »fingerprint« method is the mid-infrared range (4-12 μm). »Many chemical compounds have a unique absorption behavior in this wavelength range, which is as unique as a human fingerprint«, comments Härtelt. The wavelength range enables a clear identification of the nature and composition of molecular compounds.
Extremely variable scan speed
Quantum cascade lasers developed by Fraunhofer IAF are characterized by their extremely variable scan speed, their compact size as well as their being widely tunable. The researchers have developed a QCL that can be tuned to work at high scan frequencies or in a quasi-static mode over a wide wavelength range. This is achieved through the combination of quantum cascade lasers in an external resonator with different MOEMS based lattice scanners that work as wave selective elements. »The fastest spectrally tunable resonant MOEMS scanners allow for the scanning of one thousand complete IR ranges per second. The high scanning speed is essential for applications in which the conditions change rapidly, such as the surveillance of chemical reaction processes or moving objects«, highlights Härtelt.
QCL based measuring systems are well suited for quality control at a variety of industrial sectors, thanks to their ability to identify various chemical substances remotely and in real time. Used in the pharmaceutical, chemical and food industry the measuring systems provide information about the authenticity and purity of substances at any given time during the production process. Furthermore, the quantum cascade lasers can be used in medical diagnostics or in the security sector to test hazardous substances,. Additionally, the compact design allows for the development of mobile, and even hand-held, measuring systems.
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Topic World Food Analytics
Food analysis methods enable us to investigate the quality, safety and composition of our food. Whether in the traceability of food, the detection of contaminants or the verification of nutritional information - food analytics plays a crucial role in our health and nutrition. Welcome to the exciting world of food analytics!

Topic World Food Analytics
Food analysis methods enable us to investigate the quality, safety and composition of our food. Whether in the traceability of food, the detection of contaminants or the verification of nutritional information - food analytics plays a crucial role in our health and nutrition. Welcome to the exciting world of food analytics!
Last viewed contents
A molecule in an optical whispering gallery - With the help of a microsphere and a nanowire, single unlabelled biomolecules can be detected through light
HLA-DR5

Laser pulses create topological state in graphene
Moonstone_(gemstone)
Plant Stanols in BENECOL® Spread Included for First Time in New NIH Cholesterol Guidelines
New Superconductors Can Be Built Atom by Atom - Two new types of superconductivity
Category:EC_3.11
Synthesis with a template - Carbon-free fullerene analogue

A quick and easy way to produce anode materials for sodium-ion batteries using microwaves
Rockwell Automation Reports Third Quarter 2011 Results - Sales of $1.5 billion, up 20 percent year over year

Tracking unconventional superconductivity - Research team presents heavyweight champion