Flexible electronics without sintering
Conductive metal-polymer inks for inkjet printing
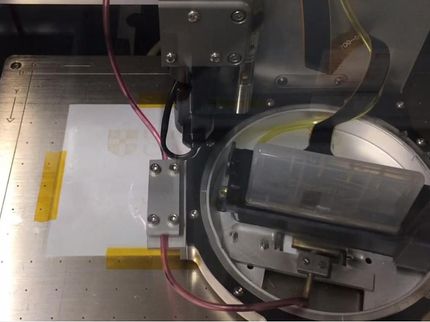
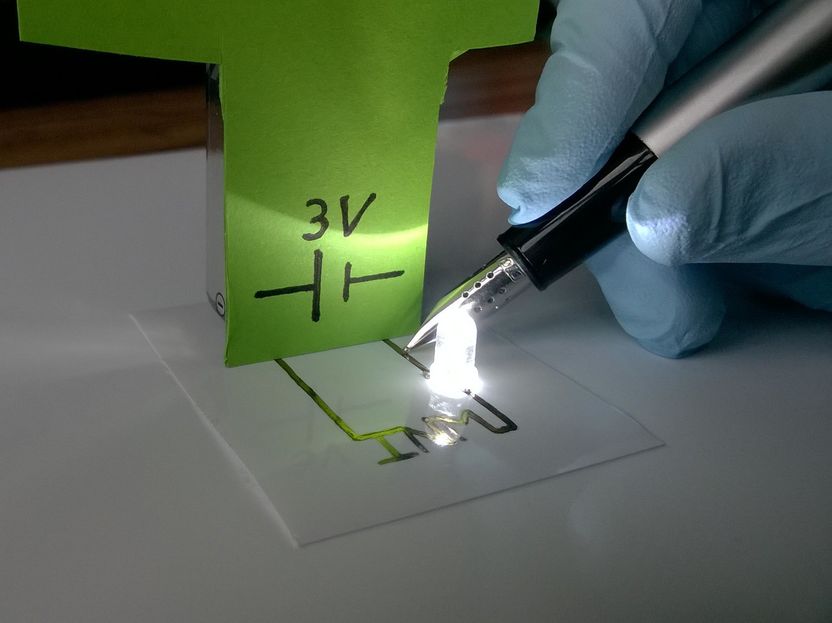
The INM – Leibniz Institute for New Materials presents hybrid inks for inkjet printing that contain metal nanoparticles coated with conductive polymers. The inks can be formulated in water and in other polar solvents and are suitable to print conductive structures on a range of substrates without any subsequent thermal or UV treatment. Standard metal inks require annealing after inkjet printing to become conductive. INM’s new inks obviate this step, making them compatible with many substrates including thin polymer foils and paper.
INM
The developers will demonstrate their hybrid inks at stand C54 in hall 5 at this year's Hannover Messe, which takes place from April 1 to 5.
Conductive inks are widely used in to print electronics. The inks presented by INM are applicable to flexible photovoltaics, lighting, touch screen electronics, wearable devices, large-area heaters, sensors, and 3D conformal antennas, among others. The inks are based on gold nanoparticles with good biocompatibility and low toxicity (FDA “generally regarded as safe”), suitable for health and biomedical applications.
“Immediate conductivity upon drying, mechanical flexibility, and good biocompatibility are important properties of our ink,” explains the INM materials scientist Tobias Kraus. “The hybrid inks contain a small organic polymer fraction that helps to maintain its electrical conductivity, even if the substrate material is bent,” Kraus continues. This enables printing on almost any substrate, like foil, paper, or textiles, since the final annealing steps at relatively high temperatures are avoided.
INM scientists have scaled the production of these hybrid inks to a level that is sufficient for small-scale production. “The scaling of nanostructured products requires optimized processes in order to maintain quality while lower prices,” says Kraus. Samples of the material are available for testing upon request.
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

New light-based method for faster and 'green' production of building blocks for medicines - "Significant breakthrough" simplifies processing of gaseous, low-weight hydrocarbons in industry
Category:EC_4.2.1
Radio chip and sensor in one
Marax
Researchers observe ultrafast processes of single molecules in liquid helium for the first time - How a molecule moves in the protective environment of a quantum fluid
Cochlear_implant
Clarification of a new synthesis mechanism of semiconductor atomic sheet - Toward the realization of next-generation flexible optoelectronic devices
John_Boot
Chalk_Emerald