Electrons use the zebra crossing
Exotic Patterns of interacting electrons at the metal-insulator transition
Since high school we know that matter appears in three different phases (solid, liquid, gas); yet the microscopic details about the transformation from one state to the other puzzles physicists until now. An international team of scientists led by Prof. Martin Dressel from the Institute of Physics (1) at the University of Stuttgart gained fascinating insights in electronic phase transitions by applying novel optical techniques.
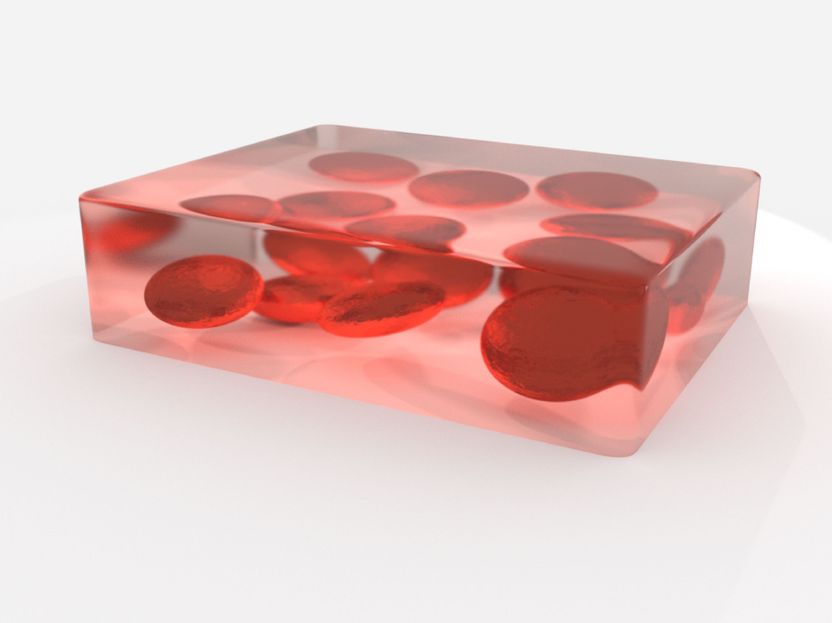
By examining the polarization of reflected light in vanadium dioxide the scientists from Stuttgart revealed the formation of sub-micrometer-size metallic droplets.
Illustration: University of Stuttgart/PI 1
The change of correlated electrons from metallic to insulating is very similar to the freezing of water into ice, i.e. transforming from liquid to solid. Since the structures at such a phase transition are typically smaller than the wavelength of visible light, it is not possible to see them by a conventional microscope. A near-field microscope, however, utilizes an atomically thin metallic tip scanning above the material’s surface to record the local optical properties. By combining such an apparatus with the capability to reach cryogenic temperatures, the physicists from Stuttgart could monitor for the first time the metal-insulator transition of a molecular crystal on the nanometer scale at temperatures as low as -138°C. They discovered a peculiar pattern of alternating metallic and insulating regions, reminiscent of the black and white fur of a zebra. The stripes have a width of less than one micrometer and occur due to the interplay of tension and strain within the crystal coupled to anomalous thermal expansion. The pattern of electronic inhomogeneity and its gradual evolution with changing temperature can be nicely modeled by a mathematical simulation.
A similarly exotic pattern of electrons was also observed in a completely different material with a metal-insulator transition: vanadium dioxide shows a sudden drop of electrical resistance when heated from room temperature above 70°C. By examining the polarization of reflected light the scientists from Stuttgart revealed the formation of sub-micrometer-size metallic droplets. They are spherical in shape and keep growing in size until they make contact at the phase transition. Cooling down again, the polarization is different from the warm-up cycle indicating that metallic regions form oblate ellipsoids, i.e. disks that become smaller in density and size until they vanish in the insulating phase; just like the melting of ice. Although a complete theoretical understanding is pending, there is evidence for a crucial influence of the layer thickness on the shape of metallic droplets.
It seems that the Stuttgart group has discovered a completely new facet of electronic materials that exhibit fascinating patterns formed by interacting electrons.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
GaN-on-Silicon for scalable high electron mobility transistors
Open_hearth_furnace

Maize and milk proteins can replace fossil fuels and metals in the production of nanostructured surfaces - Sustainably produced nanotechnology
Activin
TGF_beta
Basell launches new Metocene metallocene-based polypropylene grade targeted to customer TWIM
Eindhoven researchers observe shell growth thanks to 'ion sponge' - Revolutionary microscope technology confirms 30-year-old theory
Pfizer Acted Responsibly In Sharing Celebrex Alzheimer's Study Data With FDA - Public Citizen Charge is Misleading and Unfair to Patients
R&D for Next-Generation Solid State Batteries - Partnership between Fraunhofer and Hydro-Québec