Transition metal complexes: mixed works better
A team at BESSY II has investigated how various iron-complex compounds process energy from incident light. They were able to show why certain compounds have the potential to convert light into electrical energy. The results are important for the development of organic solar cells.
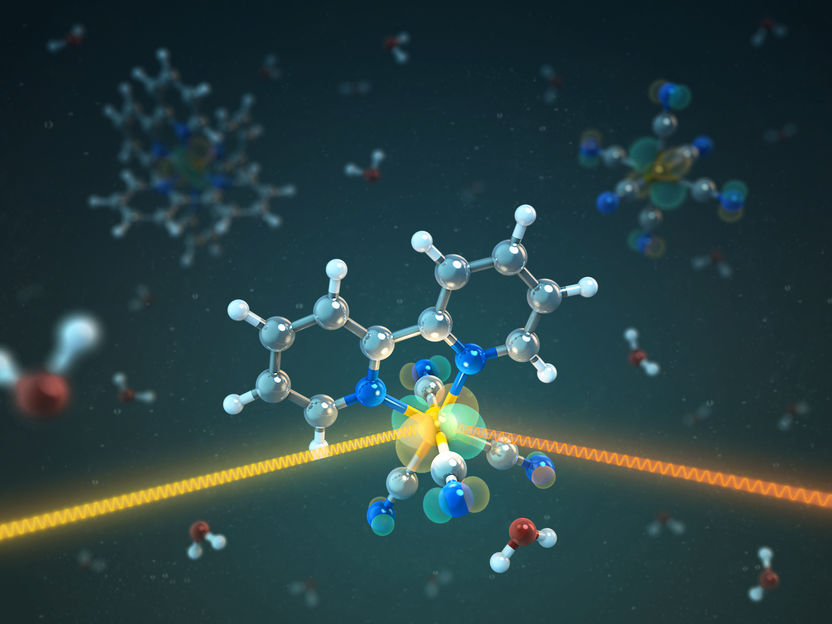
The illustration shows a molecule with an iron atom at its centre, bound to 4 CN groups and a bipyridine molecule. The highest occupied iron orbital is shown as a green-red cloud. As soon as a cyan group is present, the outer iron orbitals are observed to delocalize so that electrons are also densely present around the nitrogen atoms.
T. Splettstößer/HZB
Transition-metal complexes - that is a cumbersome word for a class of molecules with important properties: An element from the group of transition metals sits in the centre. The outer electrons of the transition-metal atom are located in cloverleaf-like extended d-orbitals that can be easily influenced by external excitation. Some transition-metal complexes act as catalysts to accelerate certain chemical reactions, and others can even convert sunlight into electricity. The well-known dye solar cell developed by Michael Graetzel (EPFL) in the 1990s is based on a ruthenium complex.
Why not Iron?
However, it has not yet been possible to replace the rare and expensive transition metal ruthenium with a less expensive element, such as iron. This is astonishing, because the same number of electrons is found on extended outer d-orbitals of iron. However, excitation with light from the visible region does not release long-lived charge carriers in most of the iron complex compounds investigated so far.
Insights by RIXS at BESSY II
A team at BESSY II has now investigated this question in more detail. The group headed by Prof. Alexander Föhlisch has systematically irradiated different iron-complex compounds in solution using soft X-ray light. They were able to measure how much energy of this light was absorbed by the molecules using a method named resonant inelastic X-ray scattering, or RIXS. They investigated complexes in which the iron atom was surrounded either by bipyridine molecules or cyan groups (CN), as well as mixed forms in which the iron centre is bound to one bipyridine and four cyan groups each.
Result: mixed forms could work
The team members worked in shifts for two weeks in order to obtain the necessary data. The measurements showed that the mixed forms, which had hardly been investigated so far, are particularly interesting: in the case where iron is surrounded by three bipyridine molecules or six cyan groups (CN), optical excitation leads to only short-term release of charge carriers, or to none at all. The situation changes only once two of the cyano groups are replaced by a bipyridine molecule. “Then we can see with the soft X-ray excitation how the iron 3d-orbitals delocalize onto the cyan groups, while at the same time the bipyridine molecule can take up the charge carrier”, explains Raphael Jay, first author of the study and whose doctoral work is in this field.
The results show that inexpensive transition-metal complexes could also be suitable for use in solar cells – if they are surrounded by suitable molecule groups. So there is still a rich field here for material development.
Original publication
"The nature of frontier orbitals under systematic ligand exchange in (pseudo-)octahedral Fe(II) complexes"; Raphael M. Jay, Sebastian Eckert, Mattis Fondell, Piter S. Miedema, Jesper Norell, Annette Pietzsch, Wilson Quevedo, Johannes Niskanen, Kristjan Kunnus and Alexander Föhlisch; Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics; 2018
Original publication
"The nature of frontier orbitals under systematic ligand exchange in (pseudo-)octahedral Fe(II) complexes"; Raphael M. Jay, Sebastian Eckert, Mattis Fondell, Piter S. Miedema, Jesper Norell, Annette Pietzsch, Wilson Quevedo, Johannes Niskanen, Kristjan Kunnus and Alexander Föhlisch; Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.



























































