New nitrogen compounds open up new possibilities for energy storage
Advertisement
An international team of researchers led by scientists at the University of Bayreuth has for the first time produced chemical compounds containing polymeric chains composed solely of nitrogen atoms. Such nitrides have an unusually high energy density and thus open up completely new prospects for future technologies of Energy storage and transmission. Technology from high-pressure and high-temperature research developed at the University of Bayreuth were used for the synthesis of the nitrogen compounds.
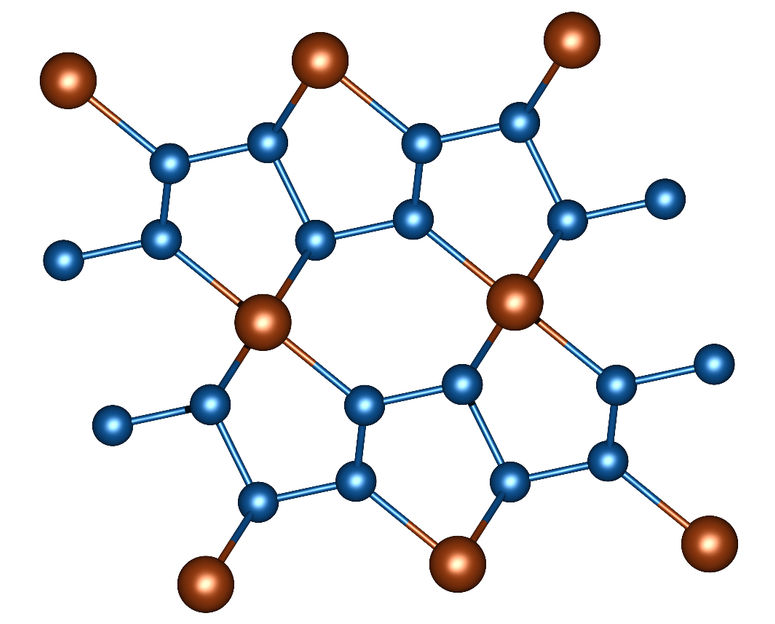
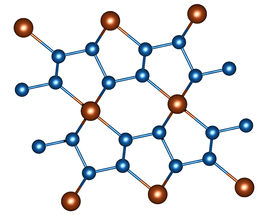
Image 1: Section of the crystal structure of FeN4. Nitrogen atoms are blue, iron atoms are brown.
Maxim Bykov
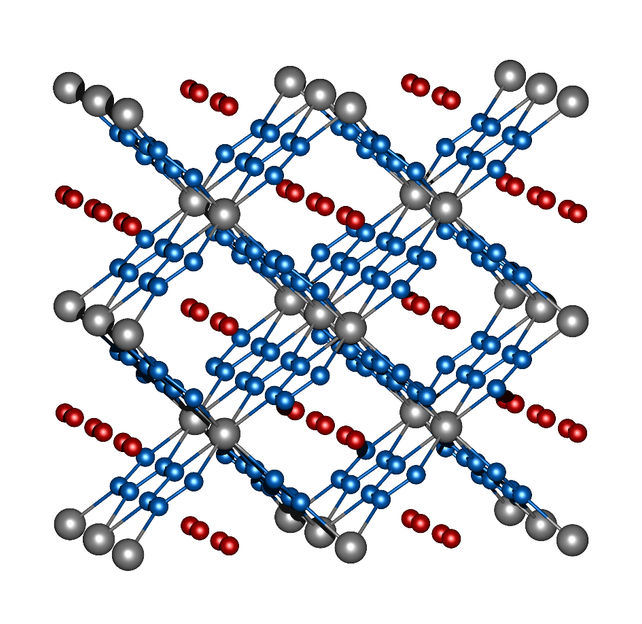
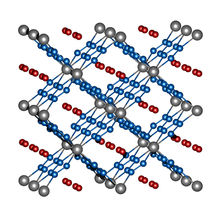
Image 2: crystal structure of ReN8·xN2. Rhenium atoms are grey, nitrogen atoms of the frame structure are blue, and the nitrogen molecules in the channels are red.
Maxim Bykov
Nitrides are a highly interesting class of inorganic materials for research due to the outstanding physical and chemical properties they often possess. For example, transition metal nitrides are characterized by extraordinary hardness, high melting points, and unusual stability. Synthesizing such nitrogen compounds, however, is rather difficult. Under normal environmental conditions, nitrogen occurs mainly as a diatomic gas N2, which only forms chemical compounds with a few other elements. The biggest hurdle in the production of nitrogen-rich compounds is that the two nitrogen atoms of N2 are linked by a triple bond, which must be broken at exceptionally high temperatures. The required temperature in each individual case depends on the nitrogen-containing compound to be synthesized.
Targeted synthesis of new nitrogen compounds under high pressure
Scientists in Bayreuth have now managed to overcome this hurdle for the first time. Using high-pressure research technologies, they have created a test environment in which the synthesis of nitrogen-rich compounds can be strategically controlled.
In a nitrogen-filled diamond anvil cell, powdered iron and – in a further series of experiments – powdered rhenium were subjected to a pressure of more than one million atmospheres (more than 100 gigapascals). At the same time, these material samples were heated to around 1500 degrees Celsius by a laser heater. Using X-ray diffraction patterns, the scientists observed how unusual compounds develop under these conditions. Iron nitride FeN4 is formed in the diamond stamp cell from iron powder and nitrogen. It is characterized by chains of nitrogen atoms in which double and single bonds alternate between nitrogen atoms (image 1).
Rhenium and nitrogen, on the other hand, form a highly unusual compound with the molecular formula ReN8·xN2. Not only does this polynitride have polymeric chains composed solely of nitrogen atoms, it also contains rectangular channels in which N2 molecules implant themselves without eliciting strong interactions between these "guest molecules" and the framework structure made of ReN8 (image 2). Both compounds, FeN4 and ReN8·xN2, represent a new class of nitrogen compounds: Metal-nitrogen frameworks.
Prospects for future energy technologies
These nitrogen compounds are of great interest for future energy research and energy technology, particularly because they have an unusually high energy density. For example, the energy density of ReN8·xN2 is many times greater than the energy density of the explosive TNT (trinitrotoluene). "The research results that we have now achieved in close international cooperation could very soon become the starting point for the development of new materials that will make a decisive contribution to the energy supply of the future. The reason is that the share of renewable energies will only increase significantly if sufficiently high yet flexible storage capacities can be created," explained Prof. Dr. Leonid Dubrovinsky of the Bavarian Research Institute of Experimental Geochemistry & Geophysics at the University of Bayreuth, who played a major role in the new studies.
Original publication
M. Bykov et al.; "Fe-N system at high pressure reveals a compound featuring polymeric nitrogen chains. Nature Communications (2018).
M. Bykov et al.; "High-pressure synthesis of a nitrogen-rich inclusion compound ReN₈·xN₂ with conjugated polymeric nitrogen chains"; Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2018).
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.