Diels-Alder reaction changes direction completely
The Diels-Alder Reaction is widely used in organic synthesis. Chemists appreciate its simplicity, reliability, and the ability to influence its course and change the conditions of the process. Several products of these transformations are used to create graphene-like materials, product vitamins, hormones, and neuromediators. Due to its durability, as well as heat and electric conductivity, graphene is used in the development of transistors, sensors, filters, and accumulators.
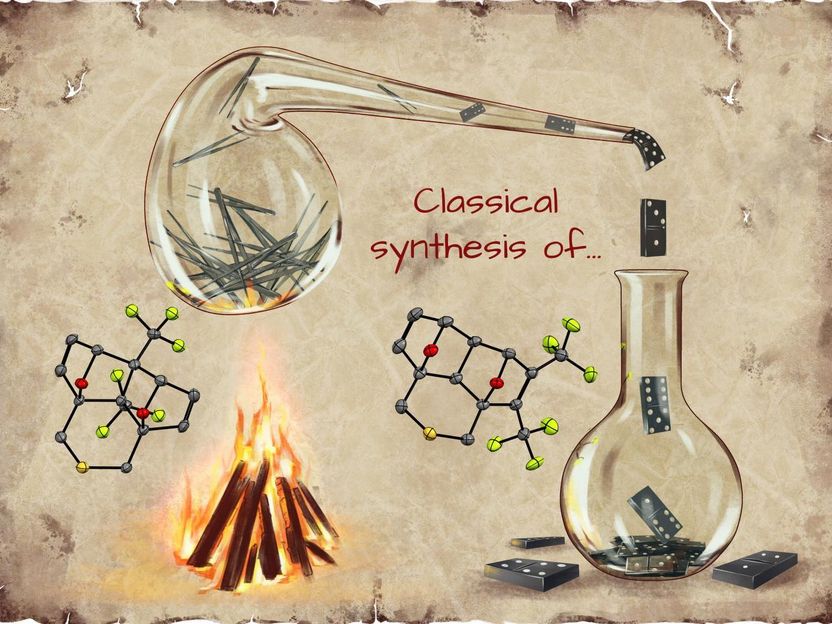
This image shows the transformation of pincer-type adducts to domino-type adducts with the raise of temperature.
Fedor Zubkov
RUDN-based scientists studied the variant of the Diels-Alder reaction in which two organic compounds (alkynes and bis-dienes) form a compound containing several six-membered cycles. The reaction proceeds different at 25-80 °C and 140 °C: the structures formed in the first case (4a,8a-disubstituted 1,4:5,8-diepoxynaphtalenes) are called by scientists "pincer-type adducts", and in the second case (2,3-disubstituted 1,4:5,8-diepoxynaphtalenes) - "domino-type adducts". In both cases the formation of a single substance is observed (rather than a mixture, like in the majority of similar cases), and only one product can be isolated with almost quantitative yield.
The initial compounds of the reaction were furfural and its derivatives. They can be obtained in almost unlimited quantities from agricultural waste: offals, sunflower seed husks and stems, sawdust and chips of several types of wood. Availability and renewability of synthetic compounds based on them are especially important due to fluctuations on the oil market and depletion of their resources in the future.
"The peculiarity of the transformation described in the work lies in the fact that they give us complete control over the composition of the products and allow us to individually obtain the necessary substances. This high level of control over the course of reaction is reached by changing only one parameter - its temperature. Almost no similar reactions have been known before our research," explained Fedor Zubkov, the head of the group, and the assistant professor of the department of organic chemistry at RUDN.
The authors of the work carried out their calculations using the density functional theory that helped determine the energy levels of both transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction and the initial and final products. These calculations match the geometrical parameters of reaction products discovered using X-ray structural analysis. Theoretical calculations carried out in the course of the study will help the scientists predict the results of similar interconversions.
In the course of the experimental work the scientists found out optimal conditions for selective reaction control, namely, the temperature and the solvent (no catalyst is required). Depending on the nature of initial reagents, the process took from 20 hours to 10 days under room temperature to 140 °C. This helped change the ratio of two isomeric compounds (i.e. the compounds with similar chemical composition but different space structure) formed during the reaction. As a result, the researchers managed to determine reaction parameters leading to the formation of only pincer-type (25-80 °C) or domino-type (140 °C) adducts.
"Besides the theoretical value, our work will be useful for processing human-generated waste and for identifying new cheap renewable sources for fine organic synthesis. In the future we plan to synthesize libraries of substances for biological screening in order to identify biologically active substances," said Ksenia Borisova, a co-author of the work, and a postgraduate at RUDN.
Original publication
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.