Tech bends light more efficiently, offers wider angles for light input
Engineering and physics researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new technology for steering light that allows for more light input and greater efficiency - a development that holds promise for creating more immersive augmented-reality display systems.
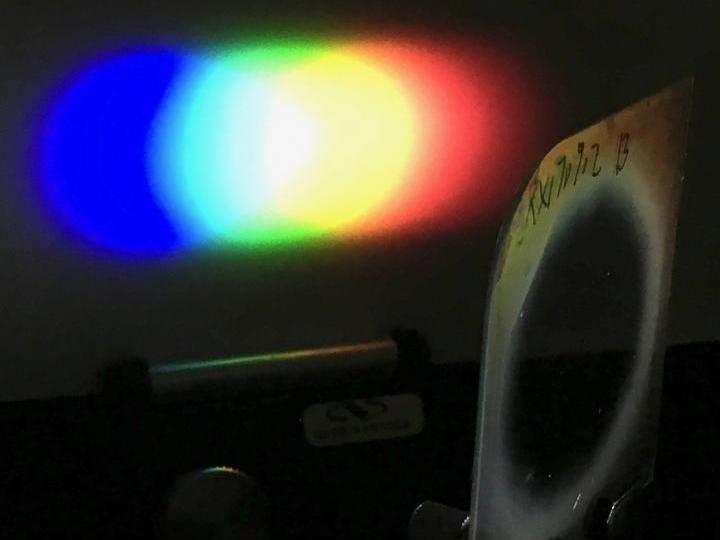

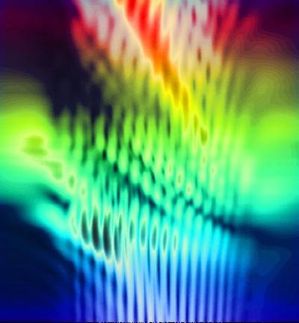
This photo shows a one-inch diameter Bragg polarization grating diffracts white light from an LED flashlight onto a screen placed nearby. Even though the difference between the light's input and output direction is very large, the grating is highly efficient for a wide set of input angles. The extremely large color separation occurs because the grating structure has a nanoscale periodic structure smaller than the wavelength of visible light. A paper on the work was published May 8, 2018, in Scientific Reports.
Michael Escuti, NC State University
At issue are diffraction gratings, which are used to manipulate light in everything from electronic displays to fiber-optic communication technologies.
"Until now, state-of-the-art diffraction gratings configured to steer visible light to large angles have had an angular acceptance range, or bandwidth, of about 20 degrees, meaning that the light source has to be directed into the grating within an arc of 20 degrees," says Michael Escuti, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper on the work. "We've developed a new grating that expands that window to 40 degrees, allowing light to enter the grating from a wider range of input angles.
"The practical effect of this - in augmented-reality displays, for example - would be that users would have a greater field of view; the experience would be more immersive," says Escuti, who is also the chief science officer of ImagineOptix Corp., which funded the work and has licensed the technology.
The new grating is also significantly more efficient.
"In previous gratings in a comparable configuration, an average of 30 percent of the light input is being diffracted in the desired direction," says Xiao Xiang, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of the paper. "Our new grating diffracts about 75 percent of the light in the desired direction."
This advance could also make fiber-optic networks more energy efficient, the researchers say.
The new grating achieves the advance in angular bandwidth by integrating two layers, which are superimposed in a way that allows their optical responses to work together. One layer contains molecules that are arranged at a "slant" that allows it to capture 20 degrees of angular bandwidth. The second layer is arranged at a different slant, which captures an adjacent 20 degrees of angular bandwidth.
The higher efficiency stems from a smoothly varying pattern in the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules in the grating. The pattern affects the phase of the light, which is the mechanism responsible for redirecting the light.
"The next step for this work is to take the advantages of these gratings and make a new generation of augmented-reality hardware," Escuti says.
Original publication
Xiao Xiang, Jihwan Kim & Michael J. Escuti; "Bragg polarization gratings for wide angular bandwidth and high efficiency at steep deflection angles"; Scientific Reports; 2018
Original publication
Xiao Xiang, Jihwan Kim & Michael J. Escuti; "Bragg polarization gratings for wide angular bandwidth and high efficiency at steep deflection angles"; Scientific Reports; 2018
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Sigma-Aldrich Recognized by BioInformatics, LLC as Having the Most Useful and Easiest to Use Online and Print Catalogs
Rockwell Automation Names New Leaders For Its Two Operating Segments
Boronic_acid
The computer recognizes chemical structures - The Fraunhofer Institute SCAI and InfoChem cooperate in developing a new software tool for the automatic recognition of images representing chemical structures
Laser-based ultrasound approach provides new direction for nondestructive testing
Merck KGaA starts world-wide launch of Chromolith HPLC Columns - The new HPLC column can separate the most complex substance mixtures into their components at maximum speed.
Two in one solution for low cost polymer LEDs and solar cells
Angiotensin_receptor
Asbestos,_Quebec

High-performance combination: Batteries made of silicon and sulphur - Research team of material scientists present an innovative, sustainable energy storage concept