Rice U. sleuths find metal in 'metal-free' catalysts
Detective work by Rice University chemists has defined a deception in graphene catalysts that, until now, has defied description.
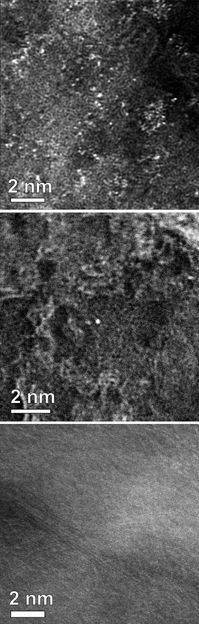
Three transmission electron microscope images of nitrogen-doped graphene show the relative presence of manganese atoms, contaminants from graphite precursors or reactants believed responsible for the material's ability to catalyze oxygen-reduction reactions, according to Rice University scientists. The top image shows many manganese atoms (white) remain on graphene that has been washed once; few on twice-washed graphene in the center image; and none on graphene washed six times at bottom. Twice-washed graphene with a scattering of manganese atoms proved best for catalysis.
Tour Group/Rice University
Graphene has been widely tested as a replacement for expensive platinum in applications like fuel cells, where the material catalyzes the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) essential to turn chemical energy into electrical energy.
Because graphene, the atom-thick form of carbon, isn't naturally metallic, researchers have been baffled by its catalytic activity when used as a cathode.
Wonder no more, said Rice chemist James Tour and his crew, who have discovered that trace quantities of manganese contamination from graphite precursors or reactants hide in the graphene lattice. Under the right conditions, those metal bits activate the ORR. Tour said they also provide insight into how ultrathin catalysts like graphene can be improved.
Because the contrast between carbon and manganese atoms is so slight, trace atoms of the contaminants can't be seen with traditional characterization techniques like X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS).
"Labs have reported 'metal-free' graphene catalysts, and the evidence they've gathered could easily be interpreted to show that," Tour said. "In fact, the tools they were using simply weren't sensitive enough to show the manganese atoms."
A more sensitive tool, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), clearly saw the interlopers among samples made by the Rice lab.
Nitrogen-doped graphene test samples were reduced from graphene oxide and then acid-washed between one and six times. With each wash, the ICP-MS scan showed fewer manganese atoms and detected none in graphene samples washed six times. By the fifth wash, the catalytic activity totally changed and showed the former activity had been due to those residual metal atoms.
The lab reported no manganese atoms were observed in any of the same samples using conventional analytical tools, including XPS or transmission electron microscopy.
The researchers characterized the samples' ORR activity and found twice-washed nitrogen-graphene was most effective. These samples tended to incorporate single atoms of manganese into the graphene structure, which facilitated full reduction of oxygen through a four-electron process in which four electrons are transferred to oxygen atoms, usually from hydrogen.
"In a four-electron process, oxygen is reduced to water or hydroxide," said Rice graduate student Ruquan Ye, the paper's lead author. "However, peroxide is formed in a two-electron process, which results in a lower diffusion-limited current density and generates hazardous reactive oxygen species." Ye said that without metal, the ORR in graphene is far less efficient.
Tour said the results should lead to investigation of the role of trace metals in other materials thought to be metal-free.
"Single-atom catalysts can hide among graphene, and their activity is profound," he said. "So what has sometimes been attributed to the graphene was really the single metal buried into the graphene surface. Graphene is good in its own right, but in these cases, it was being made to look even better by these single metal-atom stowaways."
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry enables us to detect and identify molecules and reveal their structure. Whether in chemistry, biochemistry or forensics - mass spectrometry opens up unexpected insights into the composition of our world. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of mass spectrometry!

Topic World Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry enables us to detect and identify molecules and reveal their structure. Whether in chemistry, biochemistry or forensics - mass spectrometry opens up unexpected insights into the composition of our world. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of mass spectrometry!