Printing of flexible, stretchable silver nanowire circuits
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new technique that allows them to print circuits on flexible, stretchable substrates using silver nanowires. The advance makes it possible to integrate the material into a wide array of electronic devices.
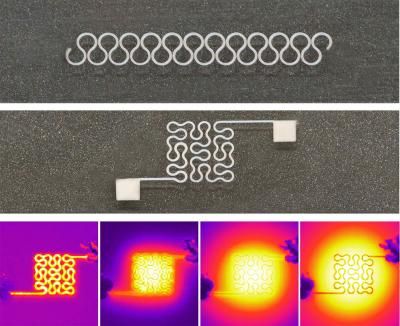
These images show two printed silver nanowire patterns: a horseshoe (top) and Peano curve (bottom) design, with high resolution. The printing technique was used to make a prototype glove containing an internal heater. The bottom shows infrared images of the wearable heater going through an on-off cycle.
Yong Zhu
Silver nanowires have drawn significant interest in recent years for use in many applications, ranging from prosthetic devices to wearable health sensors, due to their flexibility, stretchability and conductive properties. While proof-of-concept experiments have been promising, there have been significant challenges to printing highly integrated circuits using silver nanowires.
Silver nanoparticles can be used to print circuits, but the nanoparticles produce circuits that are more brittle and less conductive than silver nanowires. But conventional techniques for printing circuits don't work well with silver nanowires; the nanowires often clog the printing nozzles.
"Our approach uses electrohydrodynamic printing, which relies on electrostatic force to eject the ink from the nozzle and draw it to the appropriate site on the substrate," says Jingyan Dong, co-corresponding author of a paper on the work and an associate professor in NC State's Edward P. Fitts Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering. "This approach allows us to use a very wide nozzle - which prevents clogging - while retaining very fine printing resolution."
"And because our 'ink' consists of a solvent containing silver nanowires that are typically more than 20 micrometers long, the resulting circuits have the desired conductivity, flexibility and stretchability," says Yong Zhu, a professor of mechanical engineering at NC State and co-corresponding author of the paper.
"In addition, the solvent we use is both nontoxic and water-soluble," says Zheng Cui, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of the paper. "Once the circuit is printed, the solvent can simply be washed off."
What's more, the size of the printing area is limited only by the size of the printer, meaning the technique could be easily scaled up.
The researchers have used the new technique to create prototypes that make use of the silver nanowire circuits, including a glove with an internal heater and a wearable electrode for use in electrocardiography. NC State has filed a provisional patent on the technique.
"Given the technique's efficiency, direct writing capability, and scalability, we're optimistic that this can be used to advance the development of flexible, stretchable electronics using silver nanowires - making these devices practical from a manufacturing perspective," Zhu says.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.