Combating sulphuric acid corrosion at wastewater plants
Microbial induced concrete corrosion causes massive damage to wastewater plants
Wastewater systems are integral to infrastructure in every community. In an ideal world, they operate smoothly and are long-lasting. But biogenic transformation processes in sewage and water treatment systems are a “natural enemy” of conventional plants, frequently causing damage to concrete and metal elements that is expensive to repair. As a result, it is not uncommon for wastewater systems to have a lifespan of under ten years, before they need to be refurbished or individual components replaced. Toxic gases released during biogenic processes, such as hydrogen sulphide, also pose a significant health risk, causing a range of symptoms from irritation to respiratory failure and death.
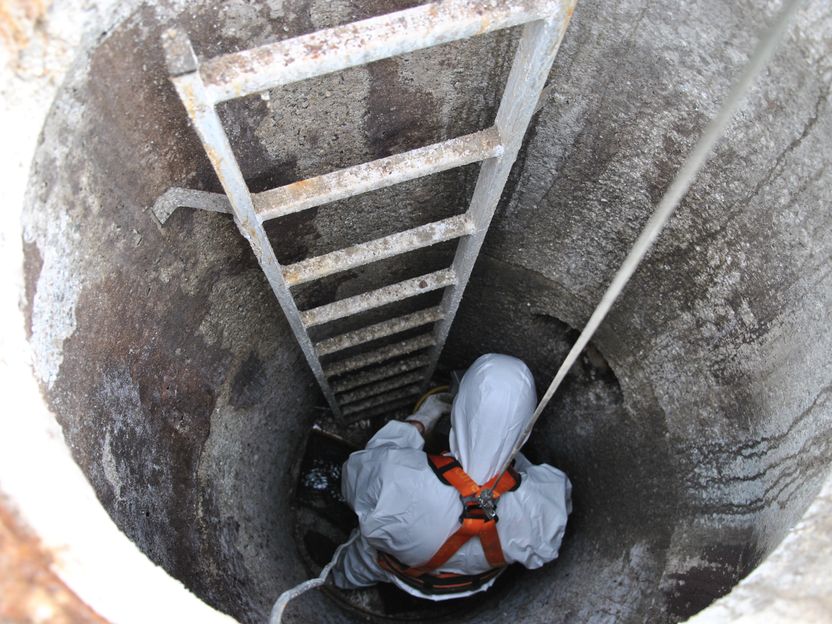

In field tests researchers from TU Graz and Graz University investigated the damage caused by microbial induced concrete corrosion.
© TU Graz
Writing in the journal Water Research, an interdisciplinary group of researchers from TU Graz and the University of Graz has outlined strategies aimed at preventing what is termed microbial induced concrete corrosion (MICC). The research team comprises two TU Graz staff members – Cyrill Grengg of the Institute of Applied Geosciences and Florian Mittermayr of the Institute of Technology and Testing of Construction Materials – as well as Günther Koraimann of the University of Graz’s Institute of Molecular Biosciences.
Microbial induced concrete corrosion: turning a blind eye not the answer
Cyrill Grengg of the Institute of Applied Geosciences at TU Graz explained: “MICC often corrodes the conventional types of concrete used in wastewater treatment plants at a rate of a centimetre or more per year. Accordingly, the concrete elements can be destroyed in a matter of only a few years, causing significant damage to wastewater systems.” According to the researchers, there is often a lack of awareness of these processes and the resulting threat to wastewater infrastructure and human health. “Closing the manhole covers and looking the other way is not the answer,” Grengg added. In Germany alone, the economic impact of wastewater system repairs is put at around EUR 450 million per year. Although no data are currently available for Austria, the costs can be extrapolated and also applied to other European countries.
Microbial induced acid corrosion (MICC) in wastewater treatment facilities results from a sequence of biogenic sulphate reduction reactions, followed by reoxidation. Initially, sulphate in pressure pipelines or standing wastewater is reduced by bacteria under anaerobic – or oxygen-free – conditions, forming hydrogen sulphide. This pungent, highly poisonous gas escapes into the sewer air and diffuses into sewer pipes and manholes. There reoxidation by autotrophic bacteria takes place on concrete walls that do not even come into contact with wastewater. These microorganisms produce sulphuric acid which reacts with concrete construction elements. As Günther Koraimann of the Institute of Molecular Biosciences at the University of Graz, who has studied these processes in detail, explains: “This leads to the vigorous formation of a biofilm on the surface of the concrete, a reduction of the pH value to below two, in other words highly acidic, and extensive formation of new minerals, mainly in the form of gypsum. The combination of these processes results in the rapid destruction of the concrete.”
Holistic solution
The Graz-based scientists worked on a holistic solution using an interdisciplinary research approach. In-depth research into the microstructural and microbiological processes was followed by the development of new MICC-resistant materials in close collaboration with the Institute of Construction and Building Materials at TU Darmstadt. In this context, geopolymer concrete proved to be particularly well suited to withstand acid corrosion. When developing this building material, resistance to acid was an extremely desirable property, as were highly antibacteriostatic surfaces, on which the research team made significant advances – microorganisms that trigger the initial oxidation process are unable to settle on such surfaces in the first place. In turn, this prevents the formation of sulphuric acid.
Florian Mittermayr of the Institute of Technology and Testing of Construction Materials at TU Graz commented: “We achieved some very promising results with materials that have a far greater lifespan than conventional types of concrete. Use of these long-lasting materials would allow operators to refurbish damaged wastewater systems, significantly extending their service life and reducing the financial burden on local government and wastewater associations.”
Original publication
Water Research 134 (2018) 341 - 352; "Advances in concrete materials for sewer systems affected by microbial induced concrete corrosion: A review"