Atomic structure of ultrasound material not what anyone expected
Advertisement
Lead magnesium niobate (PMN) is a prototypical "relaxor" material, used in a wide variety of applications, from ultrasound to sonar. Researchers have now used state-of-the-art microscopy techniques to see exactly how atoms are arranged in PMN - and it's not what anyone expected.
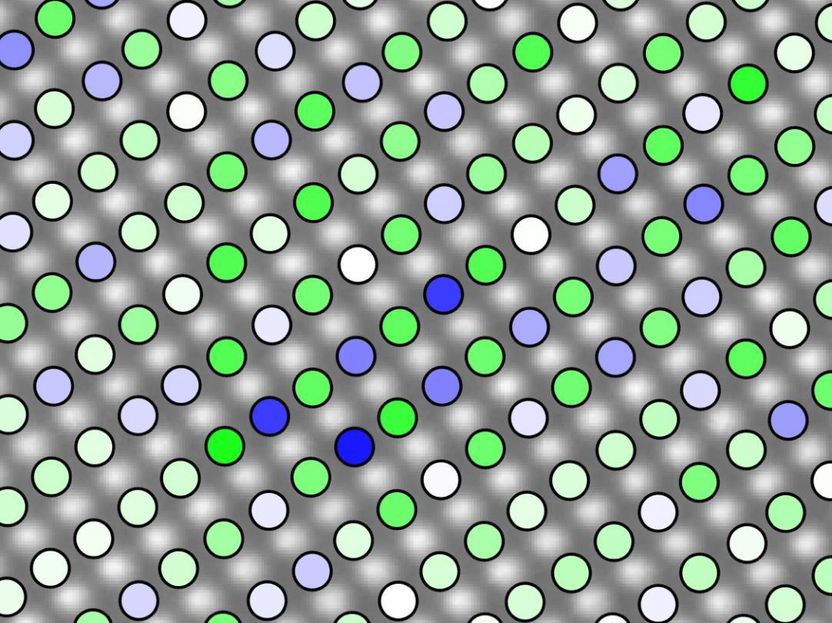
This is an atomic resolution image illustrating the chemical distribution in lead magnesium niobate. Due to mass contrast, columns of atoms rich in magnesium (blue markers) can be discriminated from columns rich in niobium (green markers).
James LeBeau
"This work gives us information we can use to better understand how and why PMN behaves the way it does - and possibly other relaxor materials as well," says James LeBeau, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work.
"What we've found is that the arrangement of atoms in PMN gradually shift along a gradient, from areas of high order to areas of low order; this happens throughout the material," LeBeau says. "That's substantially different than what conventional wisdom predicted, which was there would be alternating areas of high order and no order, right next to each other."
This information can be fed into computational models to provide new insights into how PMN's atomic structure influences its characteristics.
"This won't happen overnight, but we're optimistic that this may be a step toward the development of processes that create PMN materials with microstructures tailored to emphasize the most desirable characteristics for ultrasound, sonar or other applications," LeBeau says.
"It could also potentially offer insights into the role of atomic structure in other relaxor materials, providing similar long-term benefits for the entire class of materials."