New visible light photocatalyst kills bacteria, even after light turned off
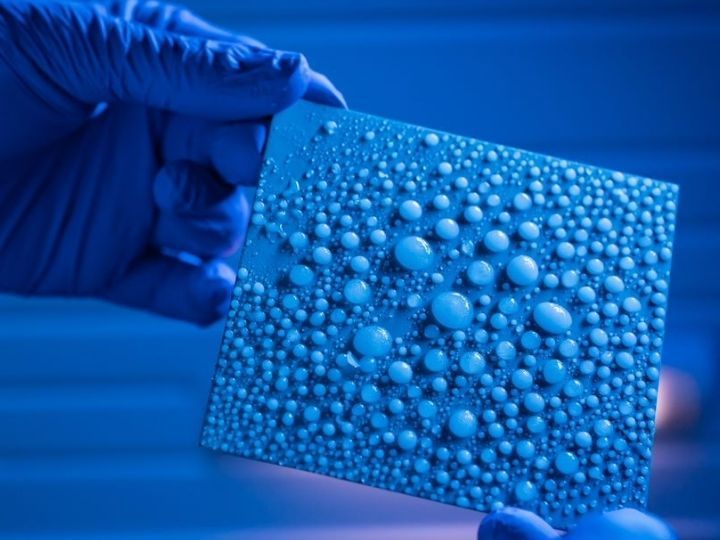
In the battle against bacteria, researchers at the University of Illinois have developed a powerful new weapon – an enhanced photocatalytic disinfection process that uses visible light to destroy harmful bacteria and viruses, even in the dark. Based upon a new catalyst, the disinfection process can be used to purify drinking water, sanitize surgical instruments and remove unwanted fingerprints from delicate electrical and optical components.
"The new catalyst also has a unique catalytic memory effect that continues to kill deadly pathogens for up to 24 hours after the light is turned off," said Jian Ku Shang, a professor of materials science and engineering at the U. of I. Shang is corresponding author of a paper in Materials Chemistry. Shang's research group had previously developed a catalytic material that worked with visible light, instead of the ultraviolet light required by other catalysts. This advance, which was made by doping a titanium-oxide matrix with nitrogen, meant the disinfection process could be activated with sunlight or with standard indoor lighting.
"When visible light strikes this catalyst, electron-hole pairs are produced in the matrix," Shang said. "Many of these electrons and holes quickly recombine, however, severely limiting the effectiveness of the catalyst."
To improve the efficiency of the catalyst, Shang and collaborators at the U. of I. and at the Chinese Academy of Sciences added palladium nanoparticles to the matrix. The palladium nanoparticles trap the electrons, allowing the holes to react with water to produce oxidizing agents, primarily hydroxyl radicals, which kill bacteria and viruses. When the light is turned off, the palladium nanoparticles slowly release the trapped electrons, which can then react with water to produce additional oxidizing agents.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents