Safer, denser acetylene storage in an organic framework
The century-old challenge of transporting acetylene may have been solved in principle by a team of scientists working at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). A NIST research team has figured out why a recently discovered material can safely store at low pressure up to 100 times as much of the volatile chemical as can be done with conventional methods.
Liu, NIST
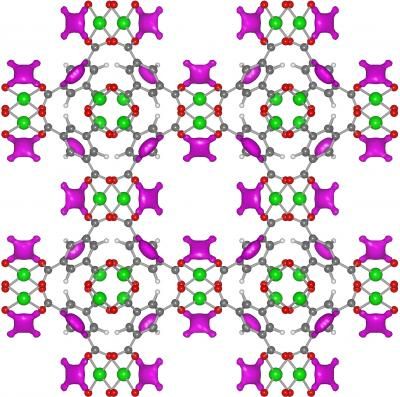
The team has probed the atomic-level workings of a metal-organic framework (MOF), a lattice-like structure made of copper oxide and benzene, that soaks up acetylene like a sponge. Using tools at the NIST Center for Neutron Research (NCNR), the scientists have shown that exposed copper atoms within the lattice give the MOF its talent at storing acetylene. The findings, according to NCNR physicist Yun Liu, could be of use to the chemical industry in the future.
“This discovery could provide substantial savings in acetylene transportation costs,” says Liu, a member of the research team, which also included scientists from the University of Texas at San Antonio.
Acetylene, widely used in decades past for welding and illumination, is now also valuable as a starting point for synthesizing a range of chemicals used in plastics and explosives. In the United States alone, several hundred thousand tons of acetylene are produced every year, but its volatility renders it difficult to transport: It becomes dangerously explosive at about 30 psi (207 kilopascal), only about twice normal atmospheric pressure. To safely store acetylene, storage cylinders have to be filled with both porous material and liquid solvents such as acetone.
The research team used neutron powder diffraction and computer calculations at the NCNR to investigate an MOF called HKUST-1, which has a sponge-like interior in which copper atoms are exposed to the air. The analysis showed that the acetylene attaches to the exposed copper by virtue of weak electrical charges, allowing the MOF to store 201 cubic centimeters of acetylene per gram of lattice at ambient pressure - comparable to the amount of similar chemicals that can be contained within a high pressure storage cylinder.
Liu says the fundamental discovery could also help scientists better understand MOFs, which could be used to store other materials. “More than a thousand of these metal - organic frameworks have been created so far,” he says. “We hope our technique will turn out to be a good way to check such materials’ properties in advance.”
Original publication: S. Xiang, W. Zhou, J.M. Gallegos, Y. Liu, and B. Chen; "Exceptionally High Acetylene Uptake in a Microporous Metal - Organic Framework With Open Metal Sites"; Journal of the American Chemical Society, Aug. 11, 2009
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

ERBAdry by CARLO ERBA Reagents
Anhydrous solvents from CARLO ERBA Reagents in a clever redesign
ERBAdry series impresses with the latest generation of septa and sealing caps

Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™ ASE™ 150 or 350 Accelerated Solvent Extractor systems by Thermo Fisher Scientific
Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE) – Maximize results and reduce errors in food analysis!
More extractions in less time using less solvent

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Tiny nanomachine successfully completes test drive

Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020 “for the development of a method for genome editing” - Genetic scissors: a tool for rewriting the code of life
Haplogroup_K_(Y-DNA)
Laser-induced graphene gets tough, with help - Combining conductive foam with other materials for capable new composites