Filling the gap?
Advertisement
A clean and efficient method for preparing thermoset composites containing ZnO nanomaterials has been developed by Scientists in the UK and Belgium.
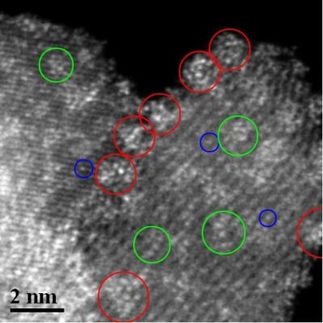
The properties of polymer resins can often be improved by filling them with inorganic particles, such as zinc oxide, which is chosen for its optical, electronic, mechanical and thermal characteristics. Unfortunately, current methods of mixing can produce very viscous mixtures due to agglomeration of smaller particles, which are pre-made and mixed with the polymer resin.
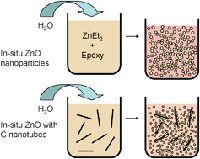
Milo Shaffer, Charlotte Williams and colleagues from Imperial College, London and a co-worker from Toyoto Motor Europe, Zaventem have developed an efficient, single pot method to prepare bulk ZnO-polymer and ZnO-carbon-polymer nanocomposites. Their aim is to build hierarchical structures, combining functional fillers in order to generate significantly improved properties. Growing the particles within the resin in this way maintains high loading fractions with low viscosity and small particle size.
‘Our synthesis applies the hydrolysis of diethyl zinc in chemically-active thermosetting resins, allowing the production of zinc oxide nanoparticles dispersed in an epoxy resin matrix,’ explains Shaffer. ‘This one pot approach allows the preparation of more complex structures, by nucleating ZnO on the surface of other fillers.’ He goes on to say that this method could be extended to other metal oxides as well as chalcogenides, including sulphides and selenides.
The next step in this approach is to control the chemistry of the interface between the growing nanoparticle and the matrix more explicitly. ‘The addition of a further component at the interface will increase complexity but offer improved performance,’ concludes Shaffer. Significant effort will also be made to scale up the procedure for use on an industrial scale.
Original article: Arántzazu González-Campo et al.; Chem. Commun. 2009
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.