© Compound InterestCyanide
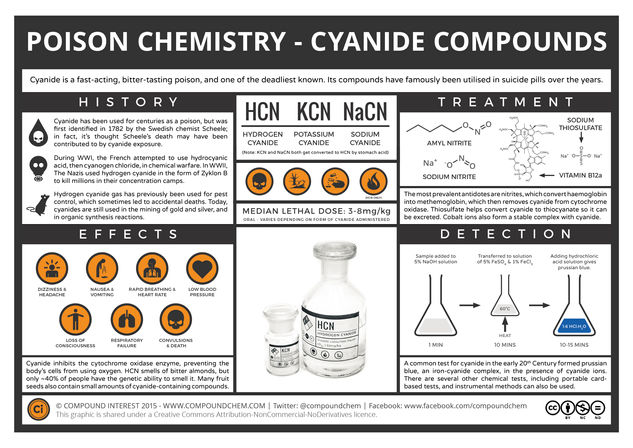
The second in the series on poisons looks at cyanide, another notorious agent of murder. It’s played a role in genocide, in suicide pills, and is also found in small amounts in the seeds of numerous fruits. So, why is cyanide so poisonous, and why are deaths from cyanide poisoning less of a rarity than those from arsenic poison in the modern day?
Cyanide is the CN– ion, and as a poison it is commonly administered as one of the three compounds shown in the graphic: hydrogen cyanide, a volatile, colourless liquid, and potassium and sodium cyanide, both white powders. Both potassium and sodium cyanide react with stomach acid to produce hydrogen cyanide, which can then go on to cause toxic effects.