© Compound InterestA Guide to the Different Types of Fat
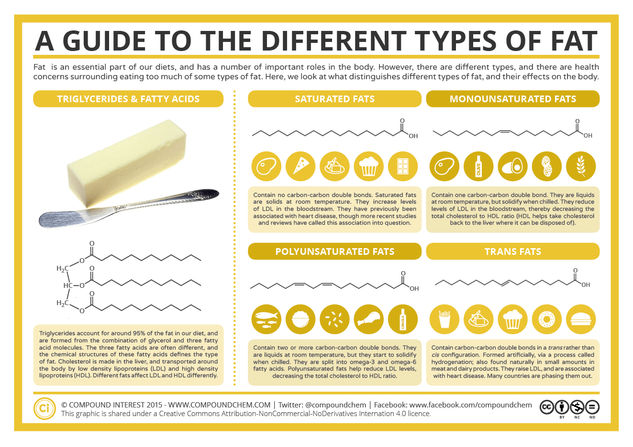
Fat is an important nutrient in our diets, but there’s a lot of talk of different types of fats, and whether these types are beneficial or harmful to our health. These different fat classifications have their roots in chemistry – and chemistry can also help explain their effects. This graphic takes a look at the different classifications, their sources, and briefly about how they act in our body.
Firstly, it’s worth emphasising that fat has an important role to play in a balanced diet. The fat in our diets is a source of some ‘fatty acids’ that are termed ‘essential’: that is, the body is unable to make them itself, and relies on our diets as their source. They’re required because they help the body absorb vitamins that are fat-soluble. We’ve looked at vitamins before in a previous post – the vitamins that fats help to absorb are vitamins A, D, E and K. Additionally, fats help provide us with energy, and they are also important for a variety of functions in the body.
Fats also play an important role in the body with respect to cholesterol. Cholesterol is a substance we produce in our livers, and it is also present in some foods. Animal cells require cholesterol to maintain their cell membranes, and it’s transported in the blood by lipoproteins. There are a number of types of these proteins, but the carriers we’re mainly interested in when discussing fats are low density lipoproteins (LDL) and high density lipoproteins (HDL).